Imaging EMR
OmegaAI
The all-in-one SaaS solution - fast, innovative, customizable - with
AI-powered imaging and instant access to medical images for patients.
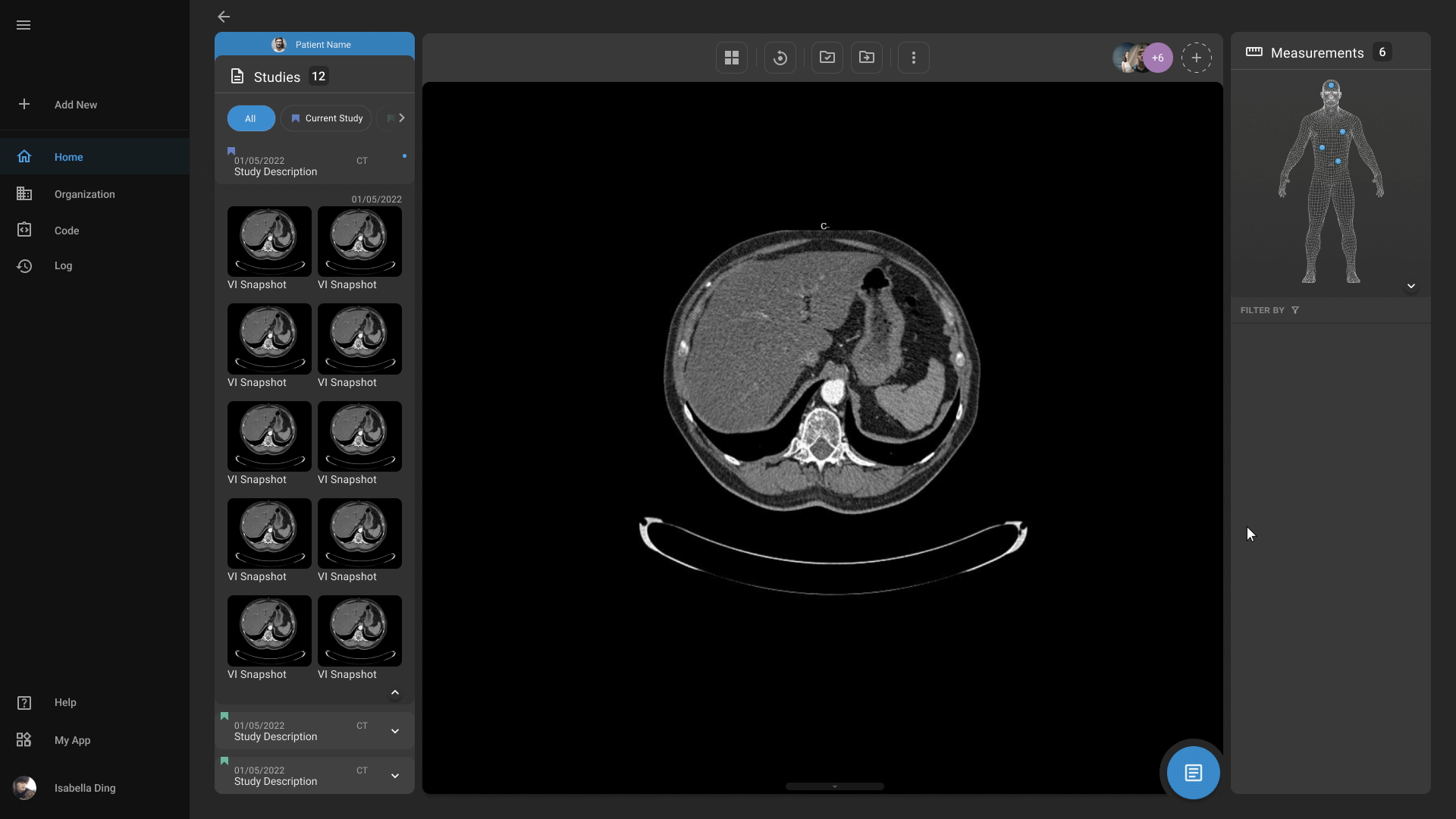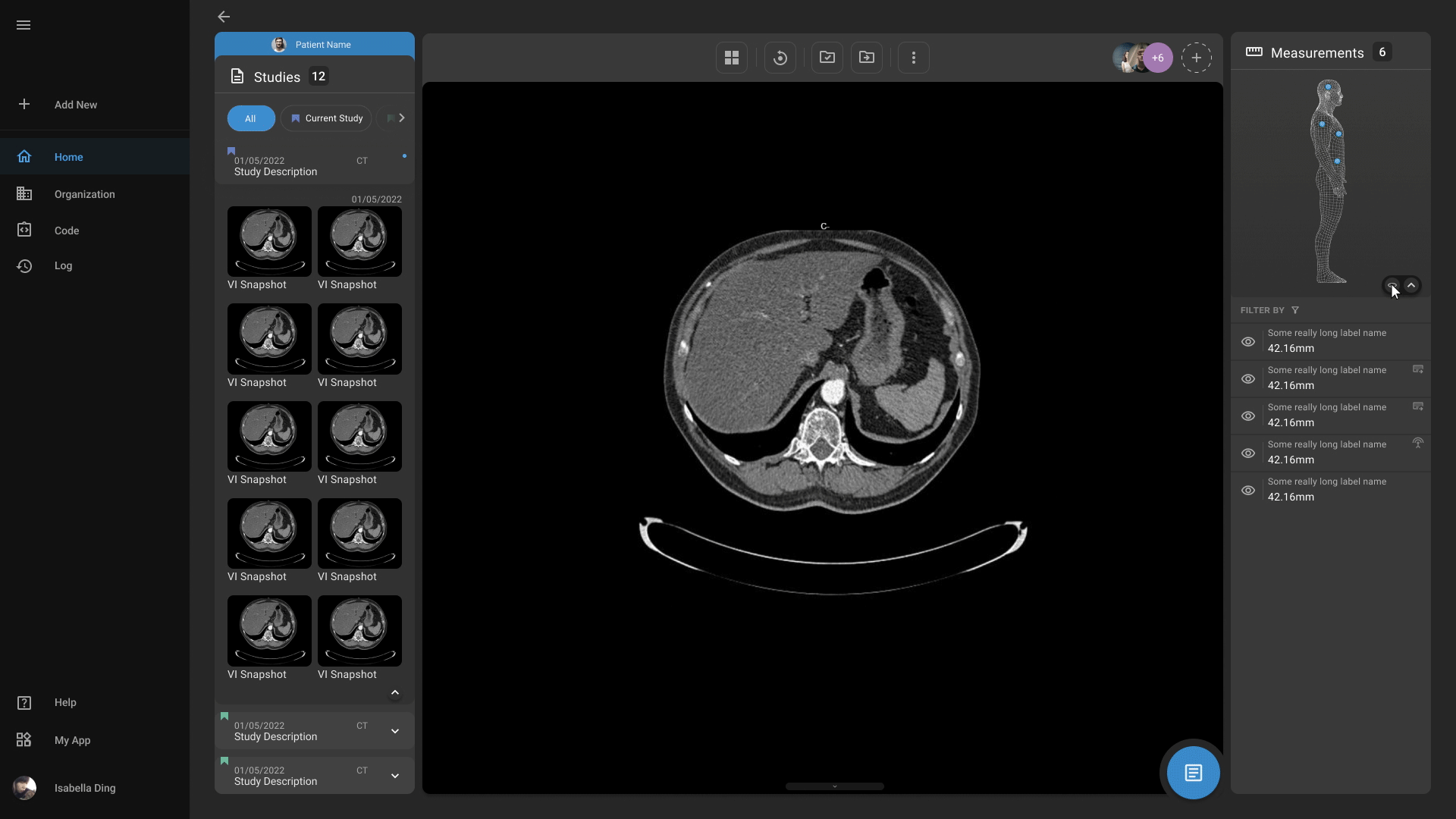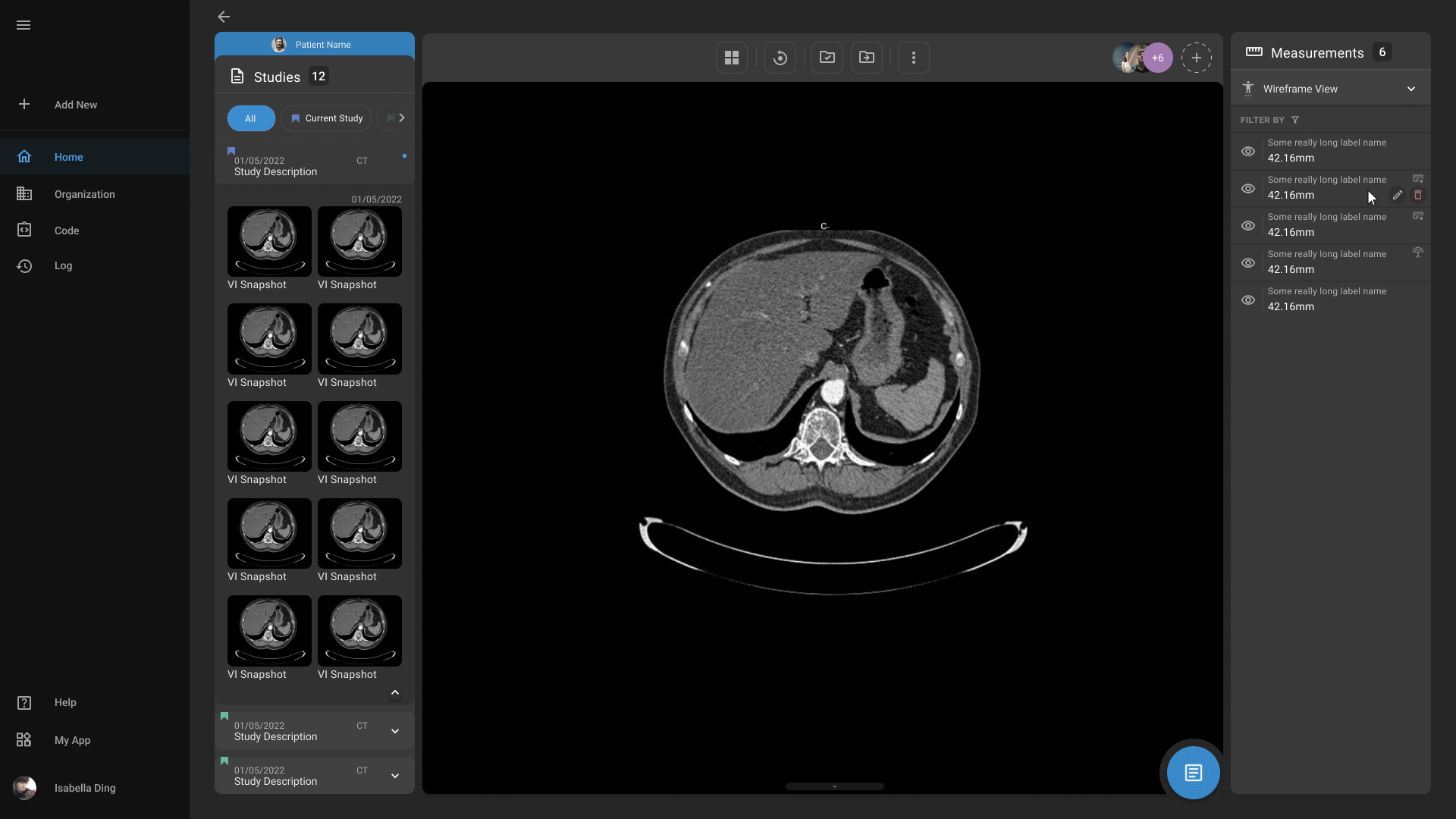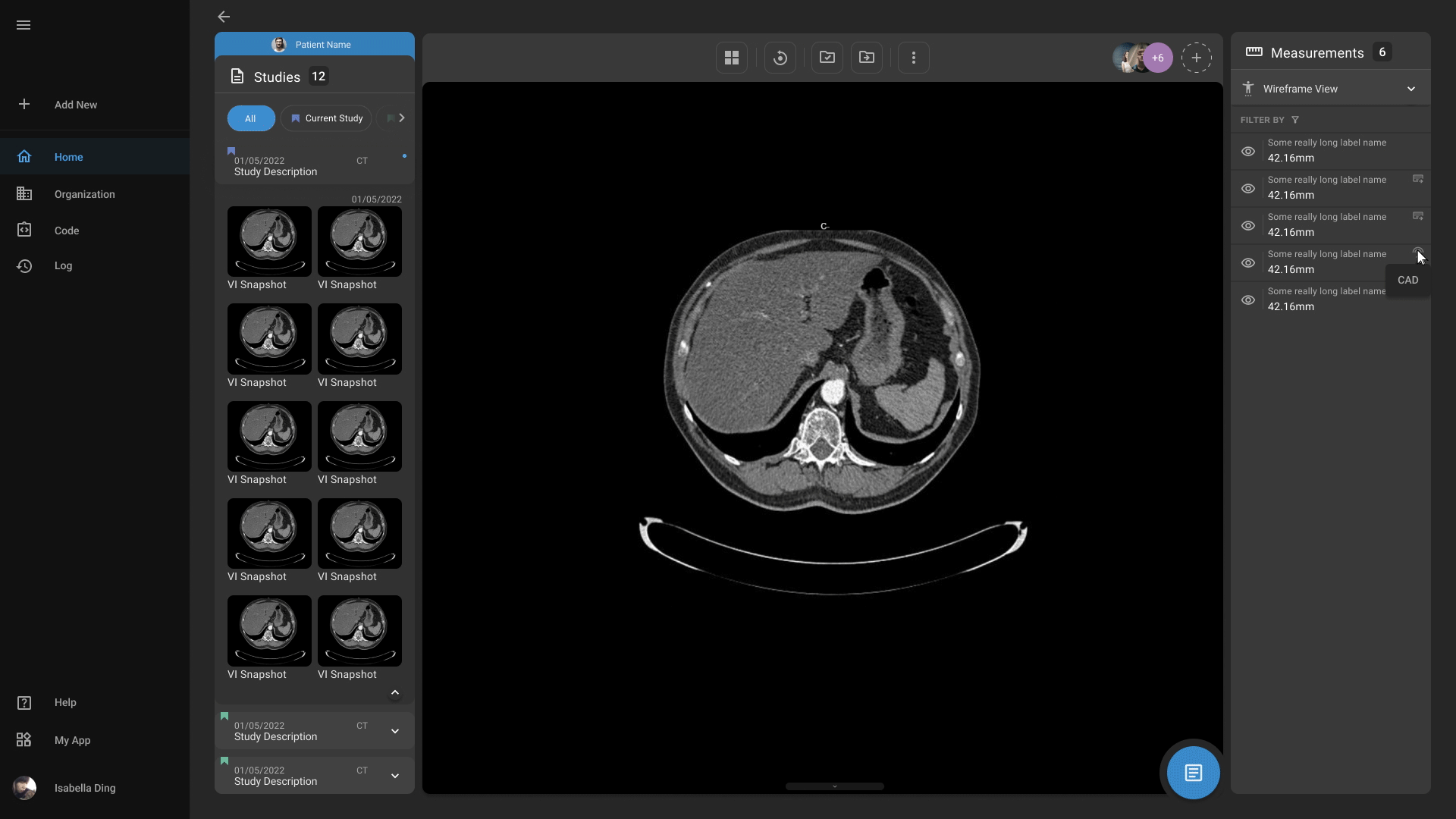
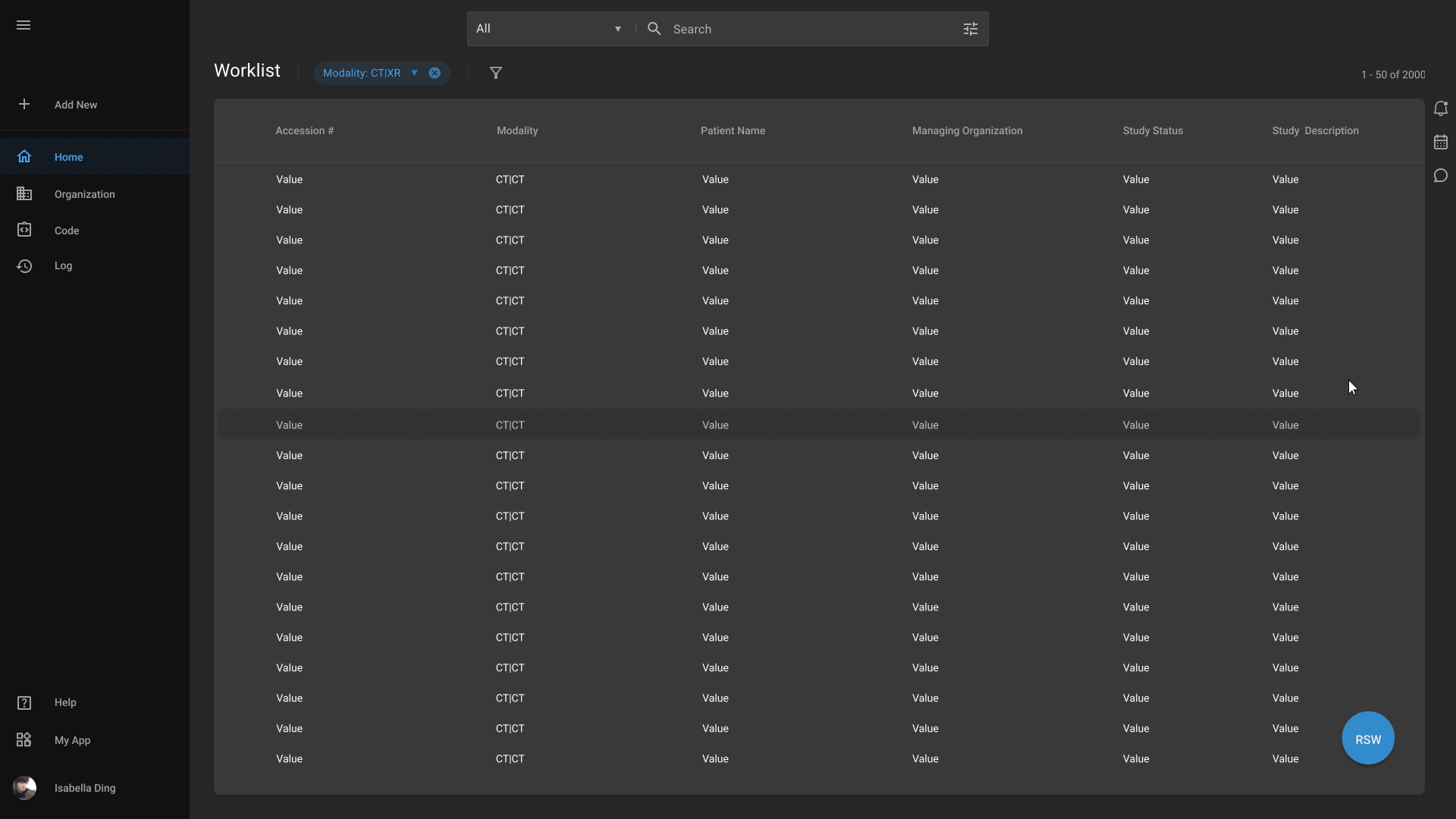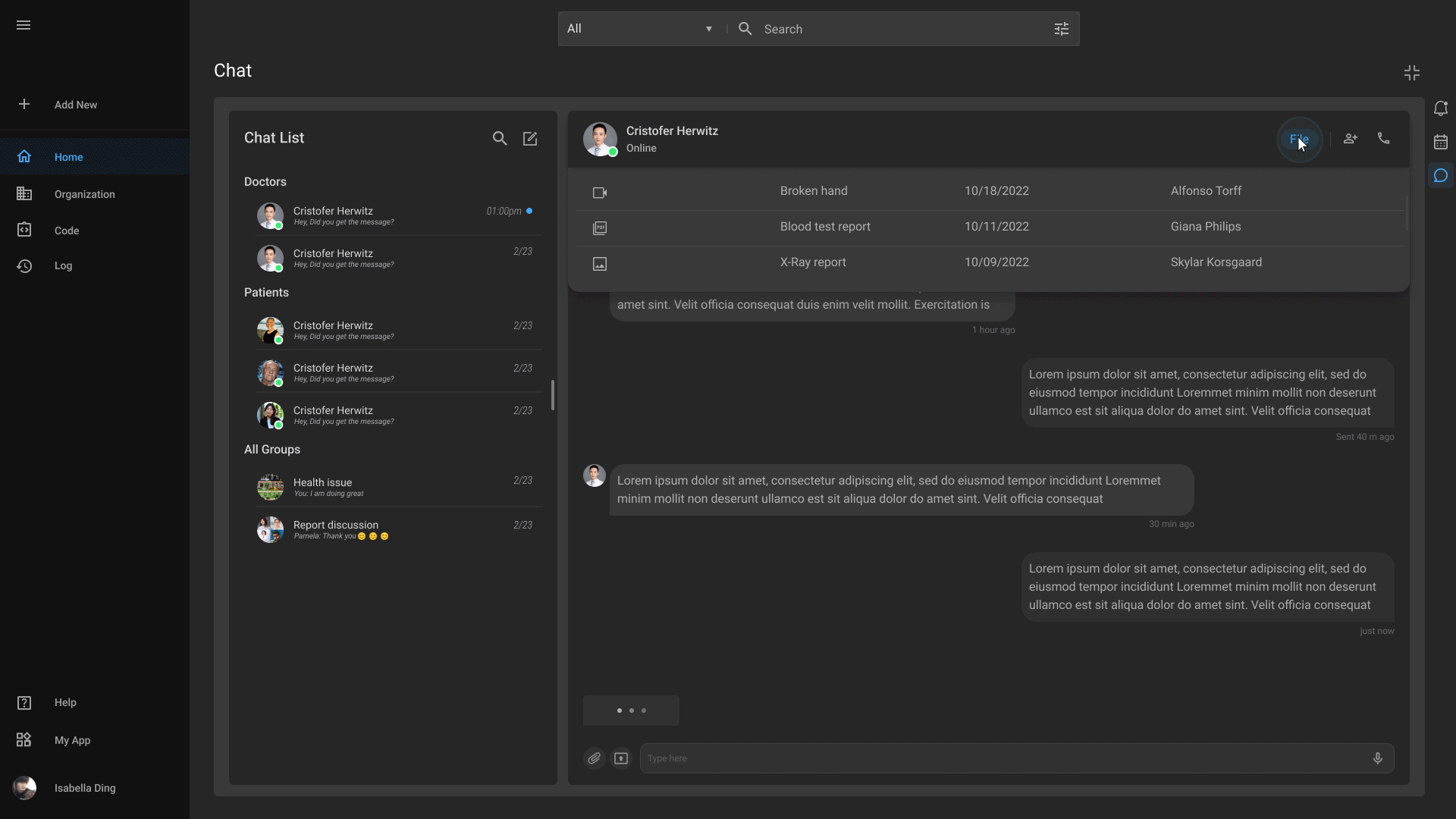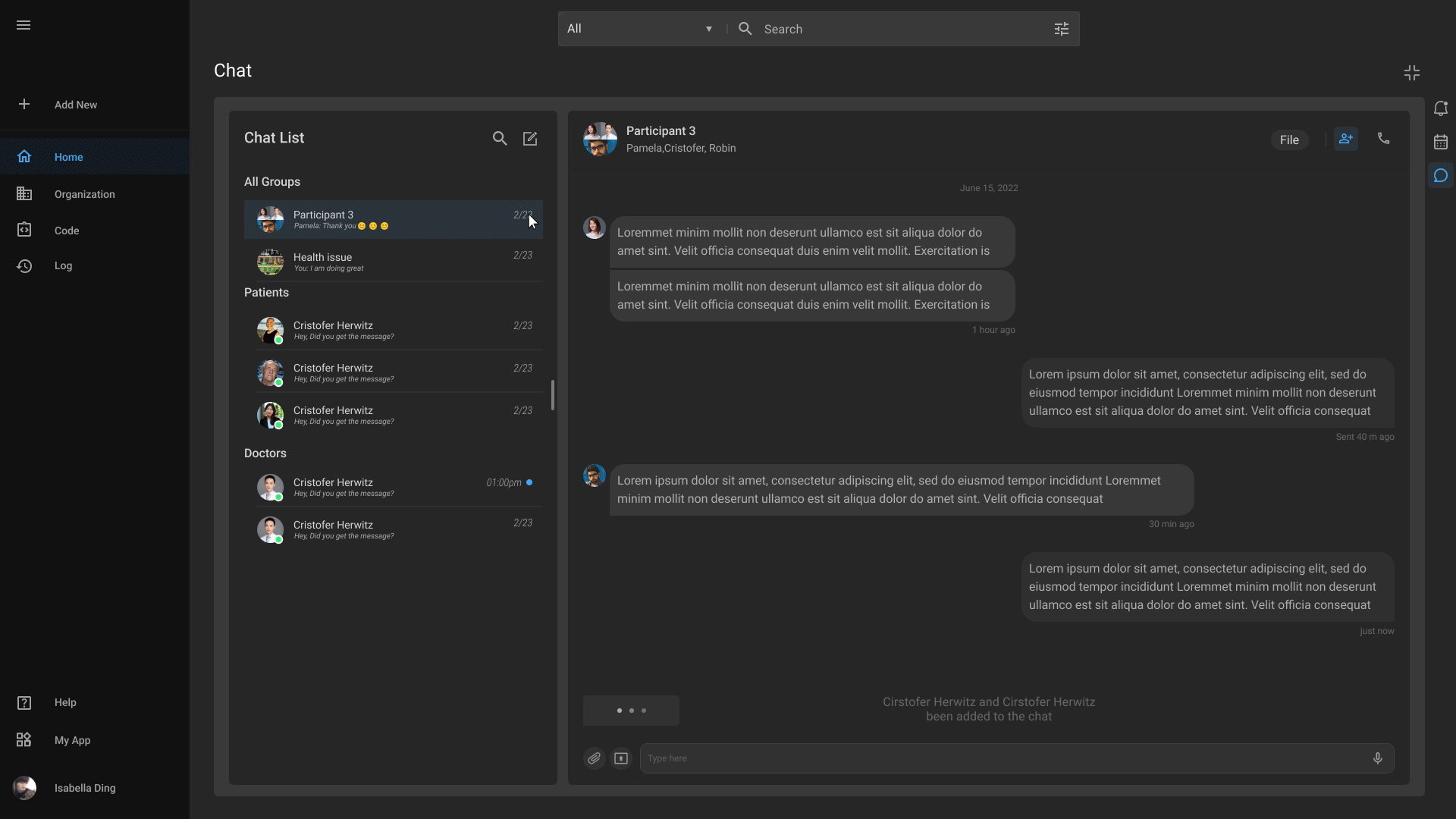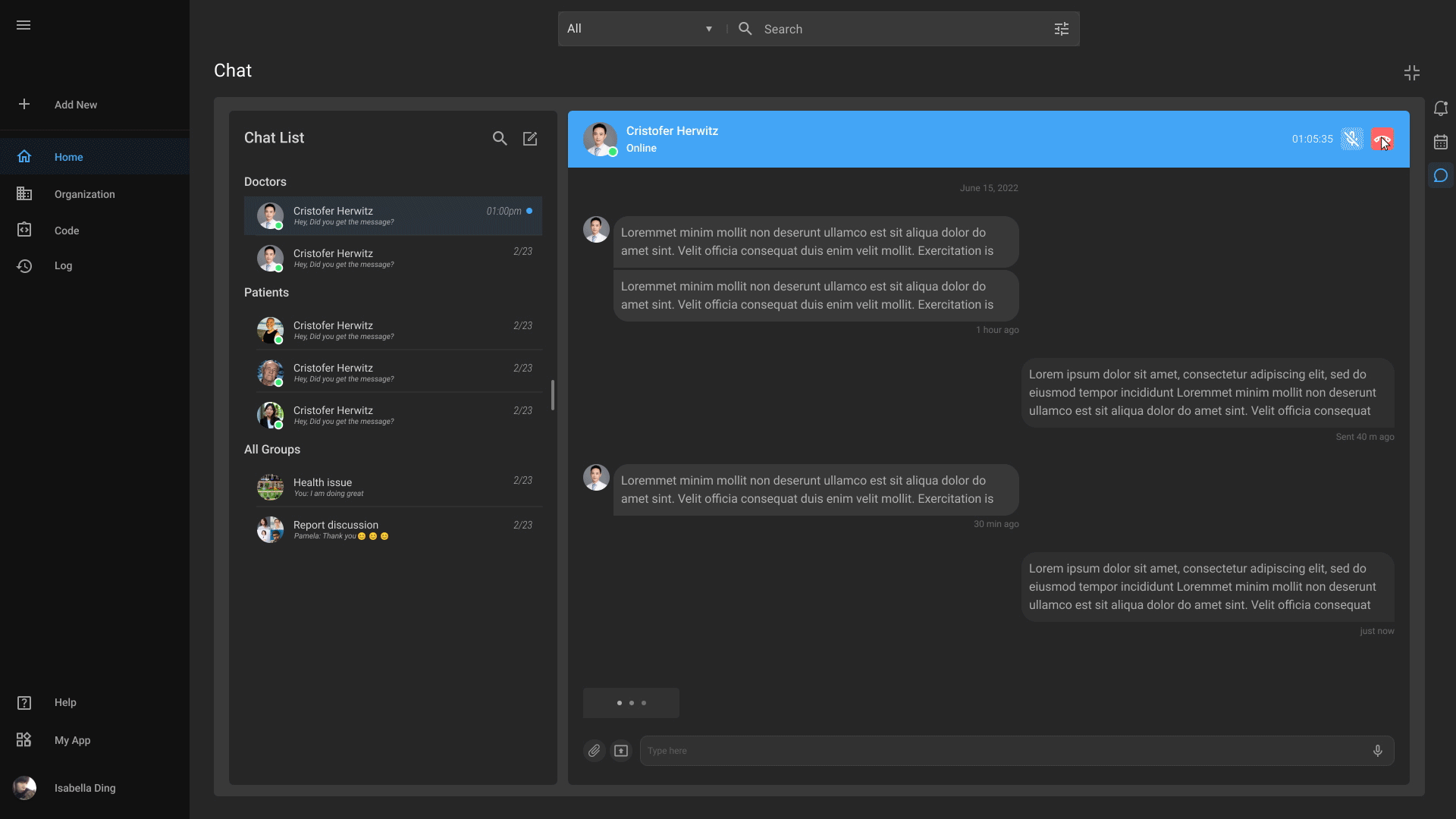
Advanced Medical Imaging
Our advanced medical imaging capabilities enables physicians to more easily detect abnormalities, highlight important findings, and quantify measurements. Our platform also offers physicians to easily markup and annotate scans according to their needs.
Diagnostic Reporting
Streamlines your workflow with advanced voice recognition tools, automated report distribution, and customizable templates.
Advanced Chat
Our advanced chat feature enables smooth communication among healthcare professionals, promotes real-time discussions, streamlines workflows, and prompts better decision-making.
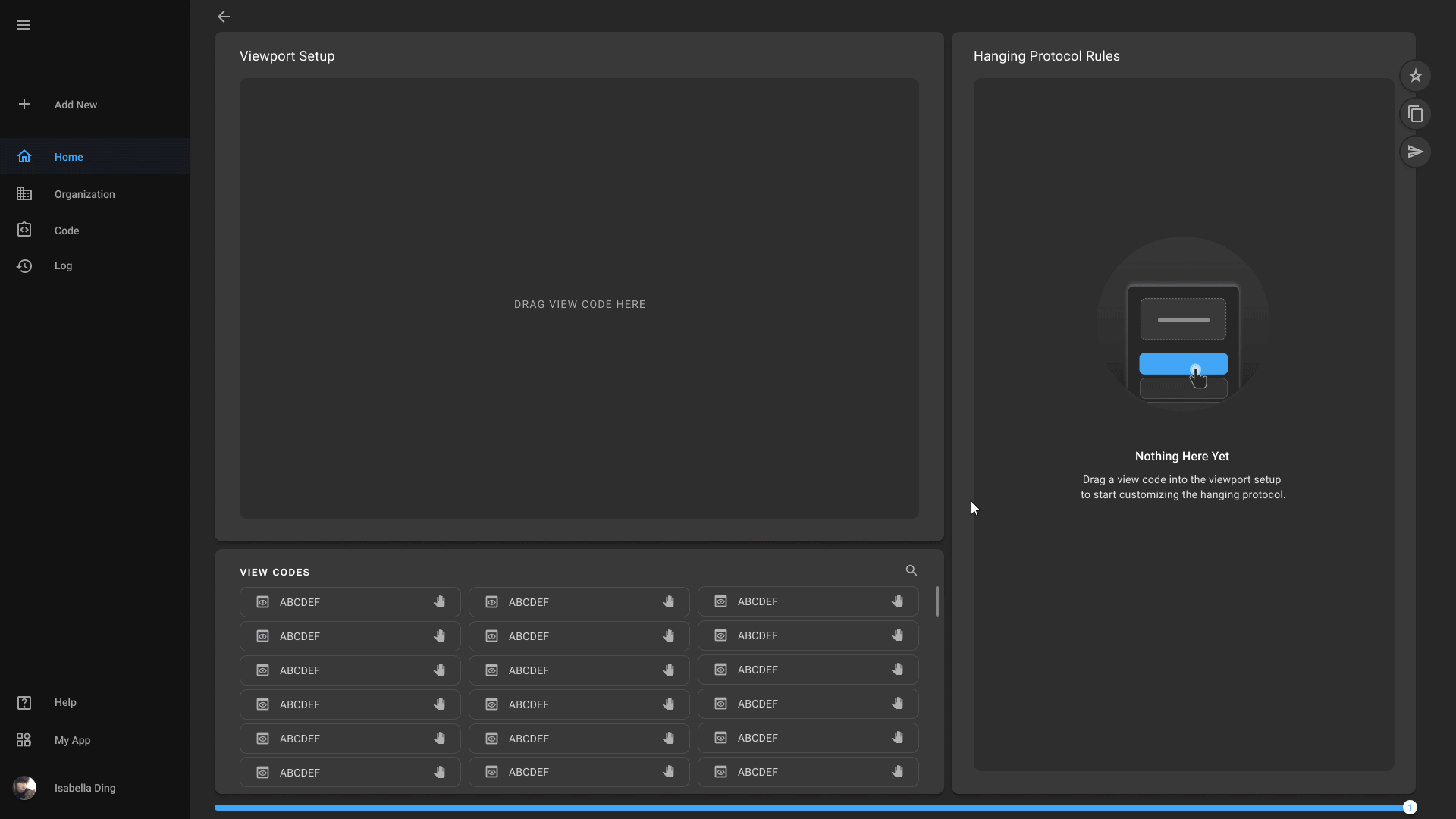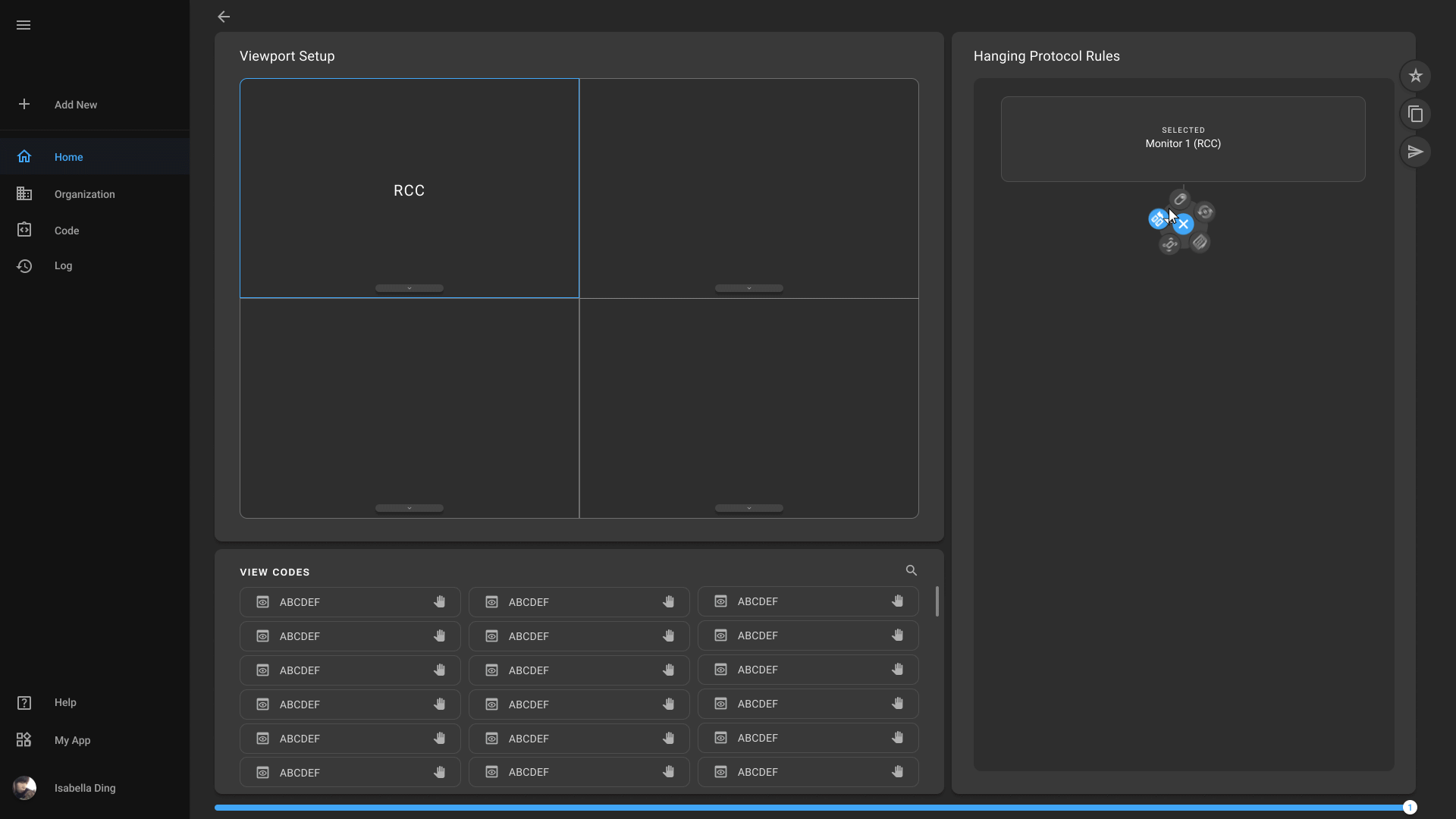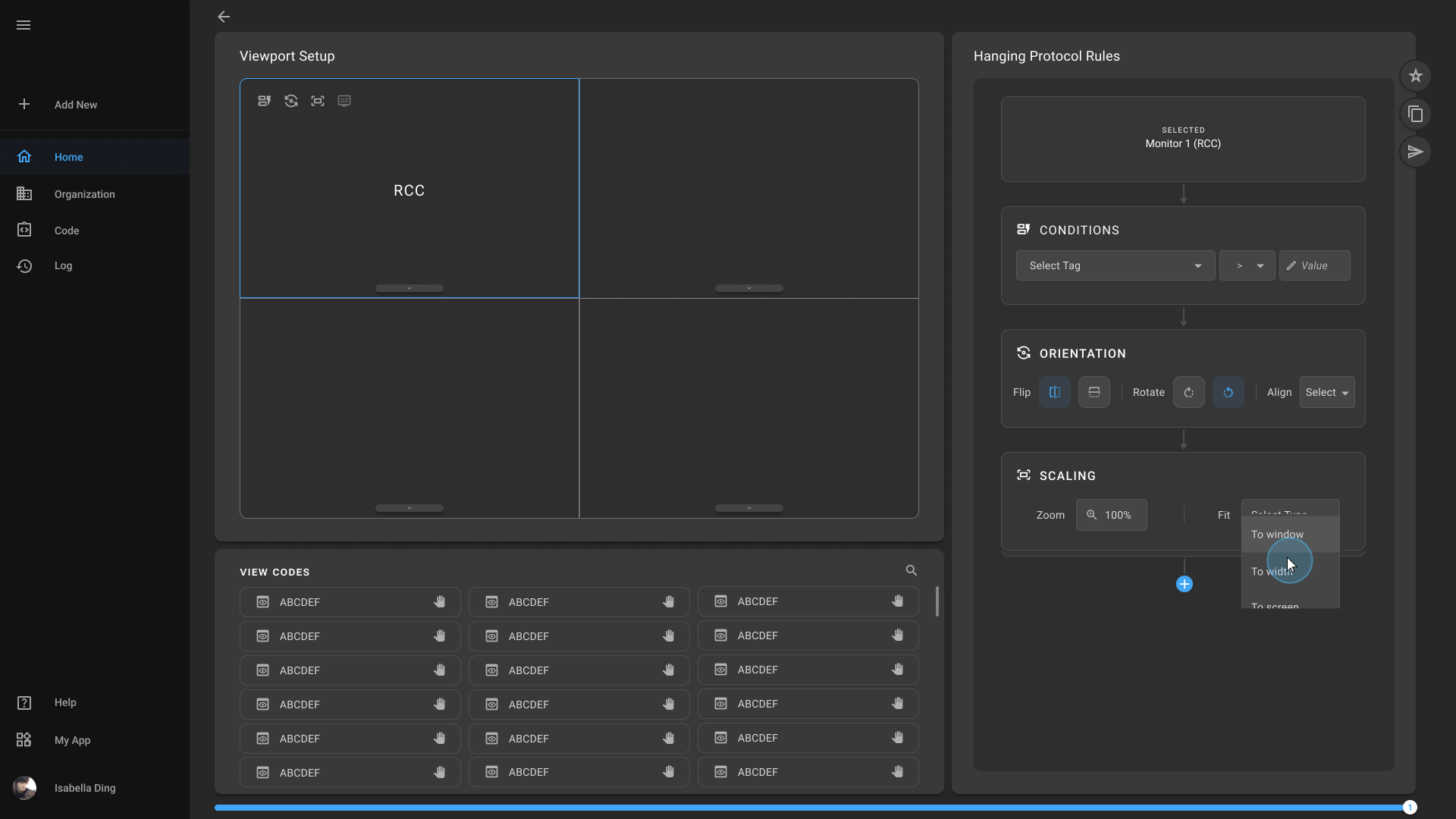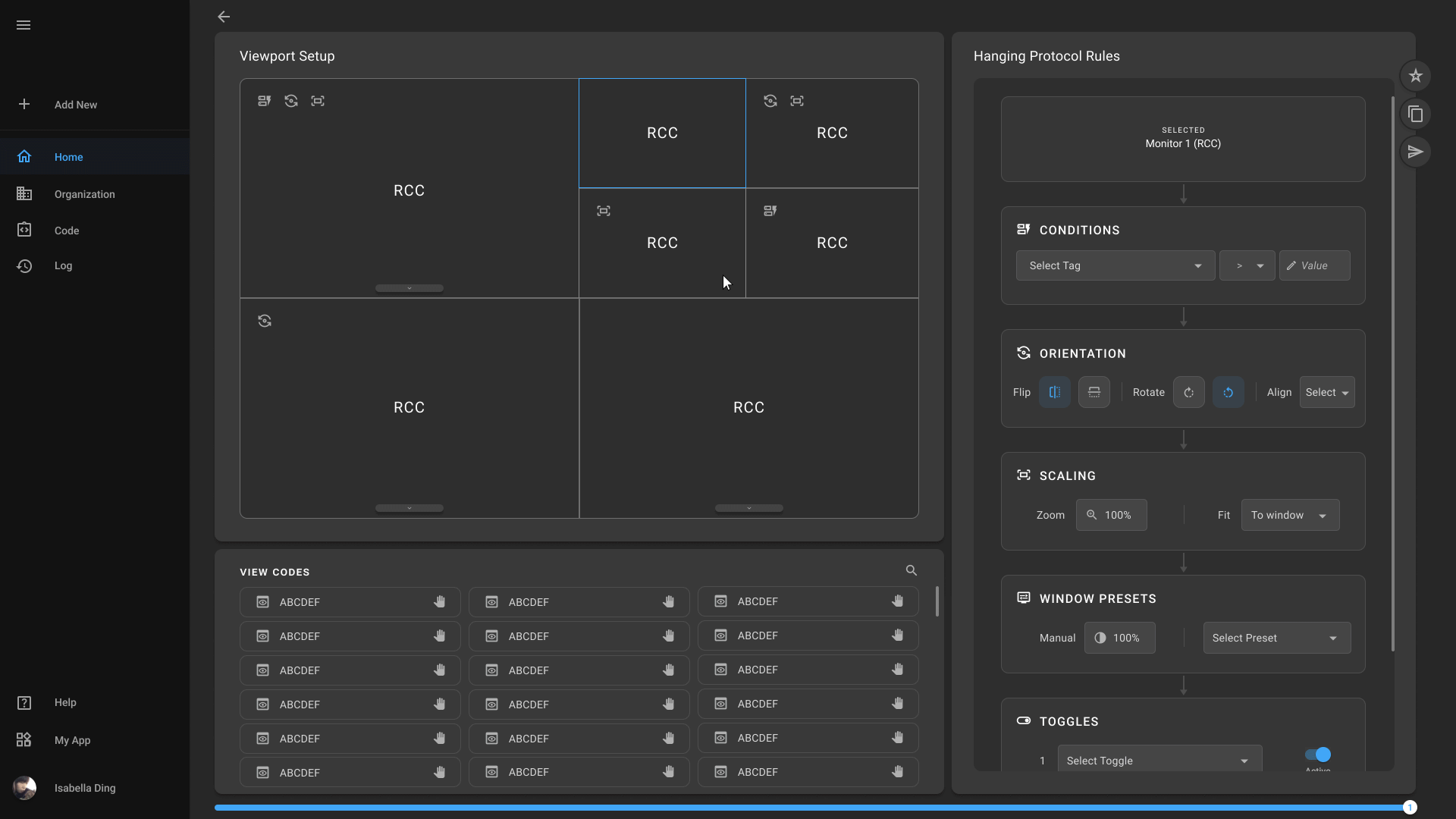
Hanging Protocol Creation
Physicians can define and save their preferred image layout, simplifying the process of reviewing multiple images and ensuring consistency across cases. You can further optimize your workflow and enhance diagnostic efficiency.
We can help
you solve
We can help
you solve
Long Scheduling Times
Our platform simplifies scheduling, eliminates long wait times, and optimizes patient appointments for a seamless healthcare experience.
Staffing Shortages
We help you overcome staffing shortages by optimizing workforce allocation, ensuring your healthcare facility has the right staff in the right place at the right time.
Patient Inaccessibility
We enhance patient accessibility to medical images and overall transparency with our user-friendly platform, empowering patients to take charge of their healthcare journeys.
Data Security Concerns
Rest easy knowing that data security is our top priority. We employ robust security measures to protect patient information, ensuring privacy and compliance at every step.
Inefficient Workflows
Streamline your operations and improve efficiency with RamSoft’s workflow solutions, automating tedious processes and eliminating bottlenecks to optimize productivity and patient care.
save patient lives
Reducing delays in patient care delivery by leveraging world-class solutions
unrivalled technology
A single database platform dedicated to automating mundane tasks, thereby reducing redundant work and data errors
Diverse Talent
We've carefully selected our talent from all over to foster a culture of innovation and collaboration
golden commitment
We believe in offering our customers the best in all aspects including quality certifications, customer-centric environment, and a honest work ethic
Say goodbye to
Our Products
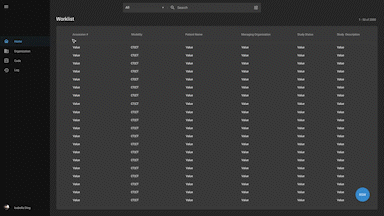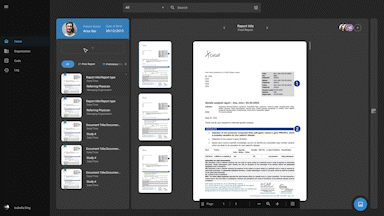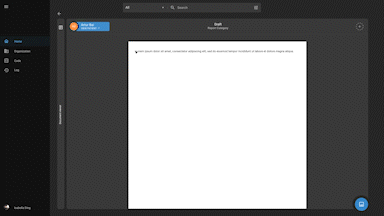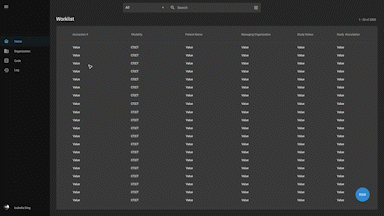
Imaging EMR for Faster, Empowered Care
Experience lightning-fast image loading and seamless accessibility with OmegaAI. Our advanced platform enables healthcare professionals to review images anywhere using the ZFP feature, leverage AI tools for accurate diagnoses, effortlessly share with other doctors, and optimize workflow through our user-friendly and highly customizable interface.
Connecting patients and doctors
With Blume, patients can gain full control over their medical imaging journey through their smartphones. They can effortlessly upload referrals, insurance information, medical history, and prior images. They can also verify eligibility and prior authorization, schedule appointments, complete forms, make payments, view and share their images and reports with doctors and family.
Unleash the Power of Business Intelligence
Experience the precision of Root's real-time, actionable reporting and analytics, delivering concise insights to fuel your decision-making process. With Root, generating comprehensive reports or creating visually appealing charts is effortless, as it utilizes an intuitive drag-and-drop interface for seamless customization.
Vast App Integrations and Customizability
Our marketplace is an innovative, centralized hub empowering users to integrate a wide range of software applications, tailoring our main platform to meet the unique needs of your organization. It eliminates the need for users to navigate multiple platforms or juggle various software systems.

"The RamSoft executive team has incredible vision on how cloud technology can transform medical imaging, and the RamSoft technical team leads applications of hyperscale cloud technology to improve timely patient care. We are incredibly proud to work with such a forward-thinking organization"
Greg Dashwood
Microsoft

"It was an easy decision to choose RamSoft over other vendors we vetted. RamSoft has a flexible and affordable system that works perfect for current and future needs. It is highly scalable and grows as we grow. Our efficiencies and output have soared. Thanks to RamSoft. ODI can continue to provide the very best in patient care for our community. We are truly grateful and will be customers for life!"
Sol Roth
Optimum Diagnostic Imaging MRI

"Our previous diagnostic imaging solution had many shortcomings, which, at times, affected our capability to provide the best care for our patients. We followed the recommendation of our teleradiology partner and were pleased to find that RamSoft's solutions are not only robust but also customizable to our specific needs without breaking the bank."
Jim Bennett
The Surgical Institute of Reading

"They routinely apply system updates and introduce new features, are keen to evolve with the regularly evolving healthcare market and are ultimately always looking for ways to enhance and improve their products"
Chloe Summerlin
DFW MRI LLC

"The people working at RamSoft are highly professional, courteous, knowledgeable, and happy to answer questions and provide training. Their implementation and IT teams are amazing."
Dr. Zareen Faiz
Downey Breast Center

"We are very impressed with RamSoft's customizations and have migrated all our customers to our new platform supported by RamSoft. Thanks to them our goals have finally been met."
Rich Owen
Medlink Imaging, U.S.

"Providing our clients with the most accurate, unequivocal,informative reports they demand is our highest priority. We found the rools we required to manage our workflow and to improve our clients' access in RamSoft's solutions."
Lisa Drazil
Specialty Teleradiology Inc.
"The RamSoft executive team has incredible vision on how cloud technology can transform medical imaging, and the RamSoft technical team leads applications of hyperscale cloud technology to improve timely patient care. We are incredibly proud to work with such a forward-thinking organization"
Greg Dashwoord
Microsoft
Customers World-Wide. Join us Today.
Talk to a sales rep to learn which of our solutions is right for you.